Democracy of Nepal
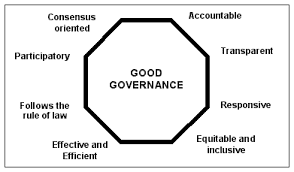
Nepal is a federal democratic republic, meaning it has a system of government where power is vested in the people, who elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf. The country has a multi-party political system, and its government operates under the framework of a constitution that ensures fundamental rights and freedoms for its citizens.
End of the Absolute Monarchy (2008): Nepal was a monarchy for centuries. In 2008, after a decade-long civil war, the monarchy was abolished, and Nepal was declared a republic. This transition marked a significant shift towards a democratic system.
Constitution of Nepal (2015): After years of political instability and conflict, Nepal promulgated a new constitution in 2015. The constitution set up a federal democratic republic, dividing the country into seven provinces, and guaranteeing the fundamental rights of citizens, including freedom of speech, the right to participate in politics, and the protection of marginalized communities.
Challenges to Democracy:
- Political Instability: Despite the establishment of democracy, Nepal has faced frequent changes in government, coalition politics, and power struggles. Political parties have often been in conflict, which has made governance difficult.
- Ethnic and Regional Diversity: Nepal is home to many ethnic, linguistic, and cultural groups, which sometimes leads to challenges in ensuring inclusive representation for all communities. The government has made efforts to decentralize power and address the concerns of ethnic and regional minorities, but tensions remain.
- Natural Disasters and Economic Development: Nepal also faces challenges related to poverty, underdevelopment, and the aftermath of the 2015 earthquake, which affected the country's ability to strengthen its democratic institutions

Comments
Post a Comment