Good Governance,principal
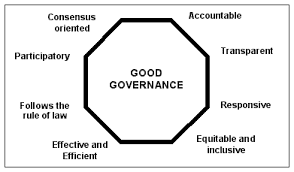
Good governance refers to the process and practices by which organizations, institutions, or governments are managed and directed, ensuring that their decisions and actions are in the best interest of the people they serve. It is characterized by transparency, accountability, fairness, responsiveness, inclusivity, and adherence to the rule of law.
Comments
Post a Comment